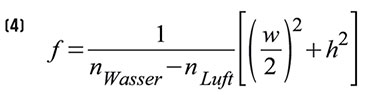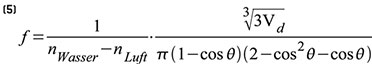Videos
Videos
 Foren
Foren
 Technik-News
Technik-News
 Wissen
Wissen
- FAQ-Datenbank
- Batterien, Akkus, Ladegeräte
- Bausätze, Lernpakete, Literatur
- Beleuchtung
- Computer-/Netzwerktechnik
- Electronic Components
- Hausautomation - Smart Home
- Haustechnik
- Kfz-Elektronik
- Klima-Wetter-Umwelt
- Messtechnik
- Modellsport, Freizeit
- Multimedia-SAT-TV
- Netzgeräte, Wechselrichter
- Sicherheitstechnik
- Telefon-/Kommunikationstechnik
- Werkstatt, Labor
- Ratgeber
- Batterien - Akkus - Ladegeräte
- Bausätze
- Beleuchtung
- Computer-/Netzwerktechnik
- Electronic-Components
- Freizeit- und Outdoortechnik
- Hausautomations-Systeme
- Haustechnik
- Kfz-Technik
- Klima - Wetter - Umwelt
- Messtechnik
- Multimedia - Sat - TV
- Netzgeräte - Wechselrichter
- Sicherheitstechnik
- Telefon-/Kommunikationstechnik
- Werkzeug - Löttechnik
- Elektronikwissen
- So funktioniert´s
- Praxiswissen
- FAQ-Datenbank
 Fachbeiträge
Fachbeiträge
- ELVintern
- Experten testen
- Praxiswissen
- So funktioniert´s
- Hausautomation - Smart Home
- Haustechnik
- Beleuchtung
- Sicherheitstechnik
- Klima - Wetter - Umwelt
- Computer/Netzwerk
- Multimedia - Sat - TV
- Telefon - Kommunikation
- Kfz-Technik
- Stromversorgung
- HomeMatic-Know-how
- Freizeit- und Outdoortechnik
- Werkzeug - Löttechnik
- Messtechnik
 Fachmagazin & Abo
Fachmagazin & Abo
Electrowetting - altes Prinzip in neuen Anwendungen Teil 2/2

Inhalt des Fachbeitrags
In Teil 1 haben wir uns überwiegend mit den physikalischen Grundlagen des EW-Effekts beschäftigt. Er besteht darin, das Benetzungsverhalten von Flüssigkeiten an Grenzflächen durch deren elektrisch steuerbare Oberflächenspannung zu beeinflussen. Jetzt geht es mit der Beschreibung ausgewählter Anwendungen weiter.
Prinzipaufbau eines Dreischicht-EWDs
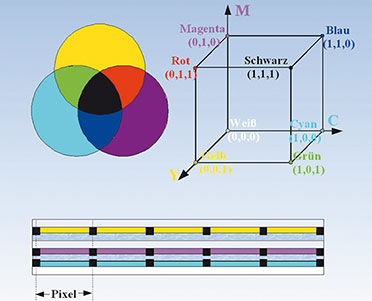 |
| Bild 9: Mit der Dreischichtenarchitektur benötigt man keine Subpixel. Jedes Pixel kann jede Farbe annehmen. |
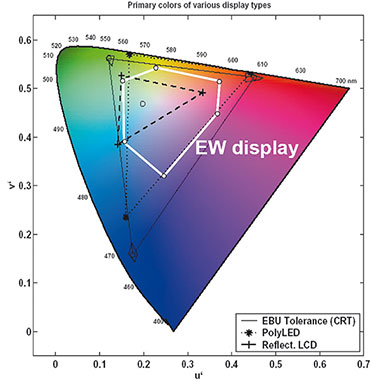 |
| Bild 10: Ein EWD hat einen erheblich größeren Farbumwandlungsfaktor (CCF) als ein reflexives LCD, wie das weiße Sechseck im Norm-Farbdiagramm beweist (1976 IEC chromaticity diagram). (Quelle: LiquaVista) |
Anwendungen
 |
| Bild 11: Ein einfaches, starres monochromes EWD zum Anzeigen der Uhrzeit (Quelle: LiquaVista) |
 |
| Bild 12: Flexible papierähnliche Displays auch für farbige Bewegtbilder sind keine Utopie. (Quelle: PolymerVision) |
 |
| Bild 13: Kleines Gehäuse – großes Display: Mit flexiblen EWDs kann die Quadratur des Kreises gelingen. (Quelle: PolymerVision) |
Mikrofluidische Systeme
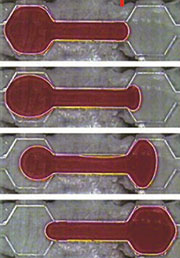
Der Begriff Mikrofluidik beschreibt die Technologien (Methoden und Komponenten), die geeignet sind, kleinste Flüssigkeitsmengen im Submillimeterbereich zu bewegen, zu dosieren und zu analysieren. Eine weit verbreitete Anwendung hat die Mikrofluidik heute in den Druckköpfen von Tintendruckern mit Inkjet-Technologie, wo winzigste farbige Tintentröpfchen mit wenigen Pikoliter Inhalt (1 Pikoliter = 10-12 Liter = 10-6 mm³) auf eine Papieroberfläche geschleudert werden, um dort zu einem hoch aufgelösten Farbbild zu verschmelzen. Neue Anwendungen sind winzige biochemische Analysatoren (Lab on a Chip), Dosiereinrichtungen, Pumpen, Aktoren und vieles mehr. Aber auch in der Materialsynthese vermögen mikrofluidische Systeme eine wichtige Rolle zu spielen.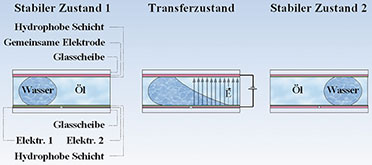 |
| Bild 14 : Tropfen lassen sich von einer aktiven Elektrode zur nächsten „verschieben“. |
 |
| Bild 15: Droplet-driven Displays speichern ein Bild auch ohne Energiezufuhr, hier ein Pixel. (Quelle: ADT-GmbH) |
Linsen mit veränderlicher Brennweite
Während im Bereich der elektronischen Schaltungen die Miniaturisierung ständig fortschreitet, stößt sie im Bereich optischer Objektive mit veränderlicher Brennweite an physikalische Grenzen. Einerseits in der mechanischen Länge, weil die Linse(n) mit fester Brennweite in ihren Abständen zueinander verschoben werden müssen. Andererseits spielt auch ein geringer Stromverbrauch eine wichtige Rolle, denn in miniaturisierten Anwendungen steht naturgemäß nur wenig Betriebsenergie zur Verfügung. Das ist der Grund, warum in modernen, superflachen Handys mit integrierter Fotofunktion bisher fast nur Objektive mit fester Brennweite (Fixfokus) anzutreffen sind, die sich nicht auf das gewünschte Objekt optimal scharfstellen lassen. Aber es gibt einen Ausweg: Der „Electrowetting Effect“ macht heute Flüssiglinsen möglich, deren Krümmung und damit Brennweite elektrisch steuerbar ist. Damit sind kleinste Optiken mit hervorragenden Abbildungseigenschaften ohne mechanisch bewegte Teile realisierbar. Die Linse im menschlichen Auge funktioniert exakt auf die gleiche Weise, nur dass ihre Verformung durch den Ziliarmuskel (und nicht durch elektrostatische Kräfte) bewirkt wird.Prinzip der Flüssiglinse
Am einfachsten zu verstehen und zu berechnen ist das optische Verhalten eines Flüssigkeitstropfens auf einer hydrophoben, ebenen Substratfläche, wie in Abbildung 4 (s. Teil 1) dargestellt. Verwendet man anstelle der in den Tropfen eingeführten (invasiven) Elektrode eine transparente flächenhafte (planare) Elektrodenringstruktur unter dem Tropfen und gestaltet das Substrat ebenfalls transparent, ist die Form des Tropfens nach wie vor beeinflussbar. Er ist nun aber als planar-konvexe Linse nutzbar, weil die Transparenz von Elektroden und Substrat und die Eliminierung der invasiven Elektrode den ungestörten Lichtdurchtritt erlauben.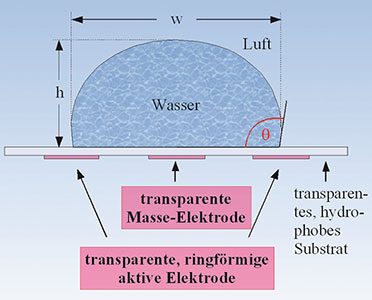 |
| Bild 16: Die Brennweite solcher planar-konvexer Tropfenlinsen lässt sich recht einfach über ihre Geometrie bestimmen. |
Technische Realisierung eines Objektivs mit Flüssiglinse
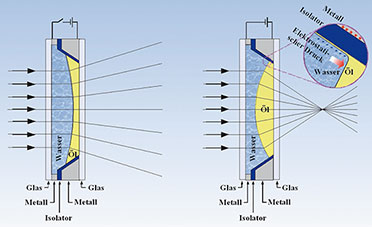 |
| Bild 17: Schnittzeichnung durch ein Objektiv mit Flüssiglinse im passiven und im angeregten Zustand (Quelle: Varioptic) |
 |
| Bild 18: Eine Flüssiglinse, kleiner als ein Cent-Stück (Quelle: Varioptic) |
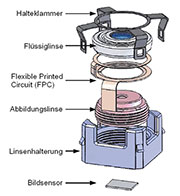 |
| Bild 19: Wenige Bauteile ergänzen die Flüssiglinse zum kompletten Autofokus-Objektiv. (Quelle: Varioptic) |
Ausblick
Der Electrowetting-Effekt wird Anwendungen finden, die über die vorstehend geschilderten weit hinausgehen. Schon heute gibt es vielfältige Anwendungen, z. B. in optoelektronischen Schaltern für die optische Signalverarbeitung, in den Life Sciences (Pharma, Pflanzenschutz auf molekularer Ebene, biologische und chemische Wirkstoffentwicklung, in den Bereichen nachhaltige Systeme, Lebensmittel und Landwirtschaft …), Nano-Technologien usw. Mit den zunehmend fachübergreifenden Forschungen und Kooperationen werden sicherlich noch viele Einsatzfelder erschlossen, die wir uns heute selbst mit viel Fantasie noch nicht vorstellen können.Quellen:
1. Johan Feenstra, Rob Hayes: „Electrowetting Displays“ http://www.liquavista.com/files/LQV060828XYR-15.pdf
2. Wolfgang Mönch, Florian Krogmann, Hans Zappe: „Variable Brennweite durch flüssige Mikrolinsen“, Photonik 4/2005
3. Karl-Heinz Blankenbach, Andreas Schmoll: „Elektrowetting – von der Physik zu Displays“, horizonte 30, Juli 2007
4. Jihwan Park: „A Liquid Lens Based on Electrowetting“, Dissertation 1997, Louisiana State University
5. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electrowetting
6. J. Heikenfeld, A. J. Steckl: „Intense switchable fluorescence in light wave coupled electrowetting devices“, Applied Physics Letters 86, 011105 (2005) http://www.ece.uc.edu/devices/Downloads/Documents/Heikenfeld_FluorELV_APL.pdf
7. adt GmbH, www.adt-gmbh.de
8. S. Kwon, L. P. Lee: „Focal length control by microfabricated planar electrodes-based liquid lens (muPELL)“, Proc. 11th International Conference on Solid State Sensors and Actuators Transducers, pp 1348–1351, vol. 1342, 2001
9. Fan-Yi Lin et al.: „Smart lens: tunable liquid lens for laser tracking“, Proc. og SPIE Vol. 6584 65840D7, Inst. of Photonics Technology, National Tsing Hua University & Inst. of Nanotechnology, National Chiao Tung University, Hsinchu, Taiwan
10. http://www.ee.duke.edu/research/microfluidics/
11. F. Mugele und J.-C. Baret: „Electrowetting: from basics to applications“, Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter 17 (2005), R705–R774
Fachbeitrag online und als PDF-Download herunterladen
Inhalt
Sie erhalten den Artikel in 2 Versionen: als Online-Version
als Online-Version als PDF (5 Seiten)
als PDF (5 Seiten)Sie erhalten folgende Artikel:
- Electrowetting - altes Prinzip in neuen Anwendungen Teil 2/2
- 1 x Journalbericht
| weitere Fachbeiträge | Foren |